Workflow
September 8, 2025
Productive Workflow
An Introduction to Git and GitHub
Luc Clair
l.clair@uwinnipeg.ca
University of Winnipeg
September 8, 2025

Preliminaries
- The necessary software to follow this lecture are
- R
- RStudio
- Git
- Created an account on GitHub
- GitHub Desktop
Introduction
What is a Workflow?
- Structured sequence of steps, tasks, and decisions that guide how a project moves from start to finish
- A good workflow is organized, repeatable, and transparent
- Helps reduce errors
- Makes work reproducible and easier to follow
Workflow Example: Applied Economic Research
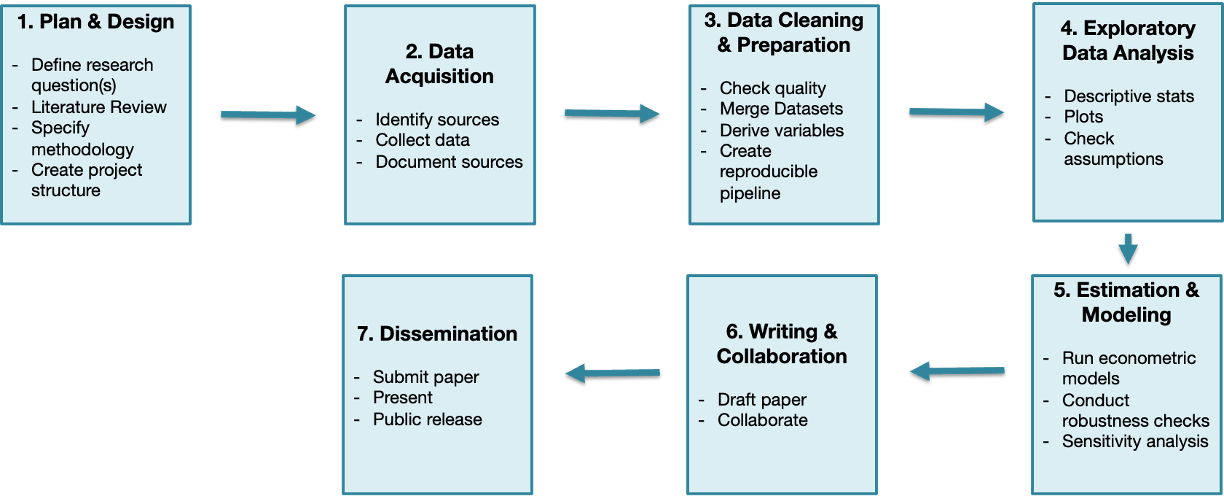
Version Control
- Version control software (VCS) is a system that helps people manage and track changes to their files over time (e.g., text documents and code files)
- It keeps track of every modification made to files, who made those changes, and when they were made
- Changes can be reverted, previous versions of files can be restored, and conflicts between different versions can be resolved
Git and Github
Git

What is Git?
- Git is a popular VCS
- Allows multiple collaborators to work on the same project simultaneously, manage changes, and share work effectively
- Git’s greatest strength is its facilitation of collaboration
- It has been described as “track changes on steroids” or as “a marriage between Dropbox and Microsoft Word’s ‘Track Changes’ feature”
Git Repository
- Git tracks the changes of a set files in a Git enabled folder or directory
- The Git enabled directory is known as a repository (repo)
- One uses Git to flag any saved changes made to files in the repository
Git Repository (cont’d)

Changes and Checkpoints
- Git can then save a version (snapshot) of repository files at a given moment in time
- This is known as a commit
- Each commit has a message explaining what was changed, keeping track of the project’s progress
Branches
- Git allows you to create branches, which are akin to an alternate version of the repository to experiment with new ideas
- Once you’re happy with the changes, you can merge these branches back into the main project
- A branch is a separate line of development
- The main branch is usually called main or master
Collaboration
- You can store your repository on a remote server (e.g., GitHub) and everyone can access it
- When someone makes changes, you can pull those changes into your local repository (folder on your computer)
- Similarly, when you make changes, you can push them to the remote server so your team can see and use them
Track and Undo Changes
- Git tracks every change you make
- If you realize you made a mistake or want to revisit an earlier version of your work, you can easily go back to previous commits
- This helps ensure you don’t lose valuable work and can always correct errors
GitHub
- GitHub is a web-based platform that helps researchers manage, share, and collaborate on code projects using Git
- It provides a cloud-based space where you can store your Git repositories and interact with other developers’ projects
- GitHub has become one of the most popular platforms for open-source and private software development
Git and Workflow
- Version control is a critical component of a productive workflow
- A recommended first-step of any workflow is to set up a Git-enabled repository for your project files and link this repository to GitHub.com
Creating a Git Repository
Creating a Git Repository
Three main ways
- Create repository on GitHub.com
- Add new repository using GitHub Desktop
- Create a new folder on your local computer and enable Git
Create Git Repository on GitHub
- Go to github.com and sign in
- On your home page, click the
![]() button
button
Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Enter the name of the repository
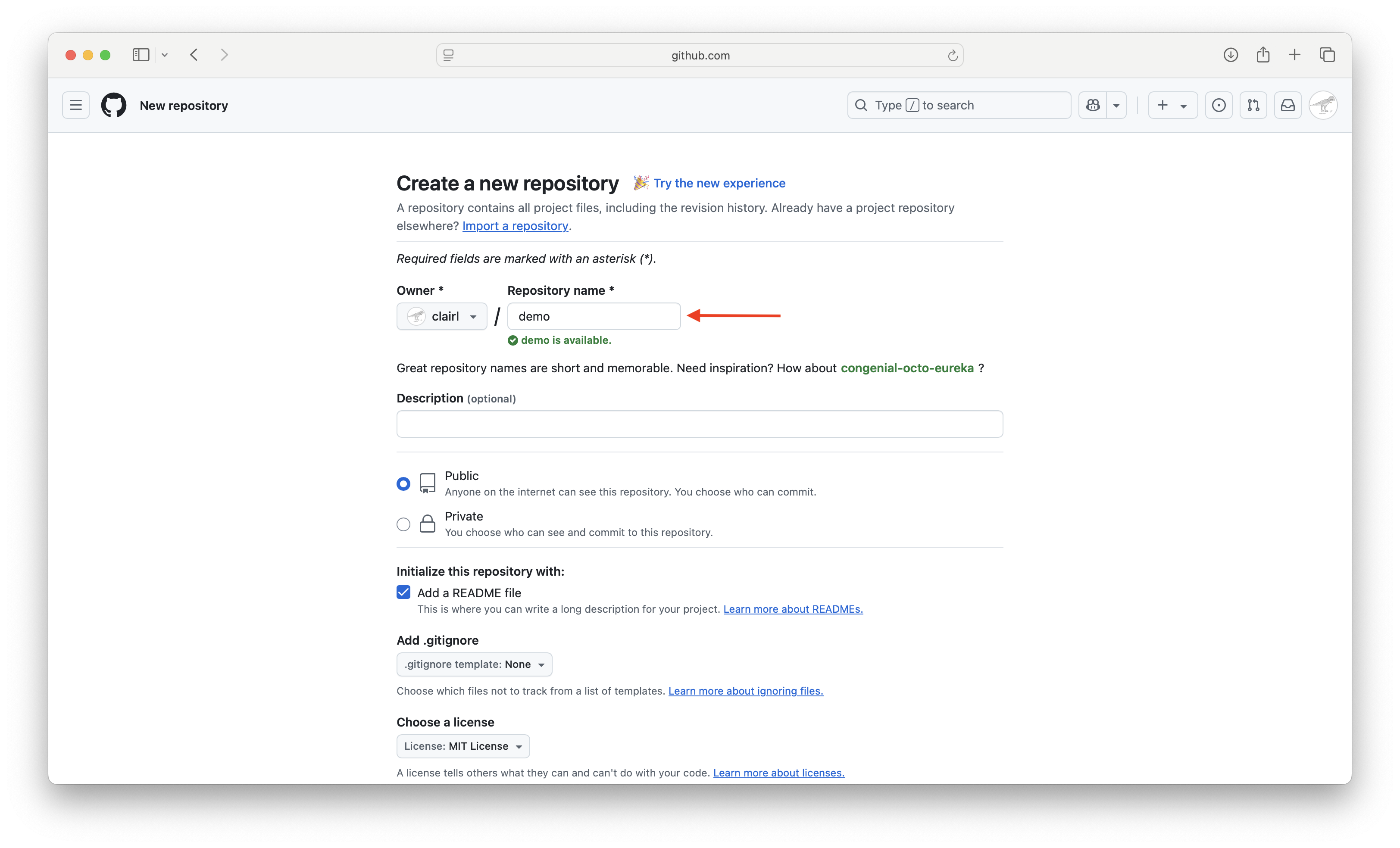
Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Choose whether you want the repository to be public or private

Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Add a README file, which gives a description of your project

Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Choose a license, then press Create
- For more on open source licensing, please visit ChooseALicense.com

Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Your repository has been created
- Here are a few things to notice
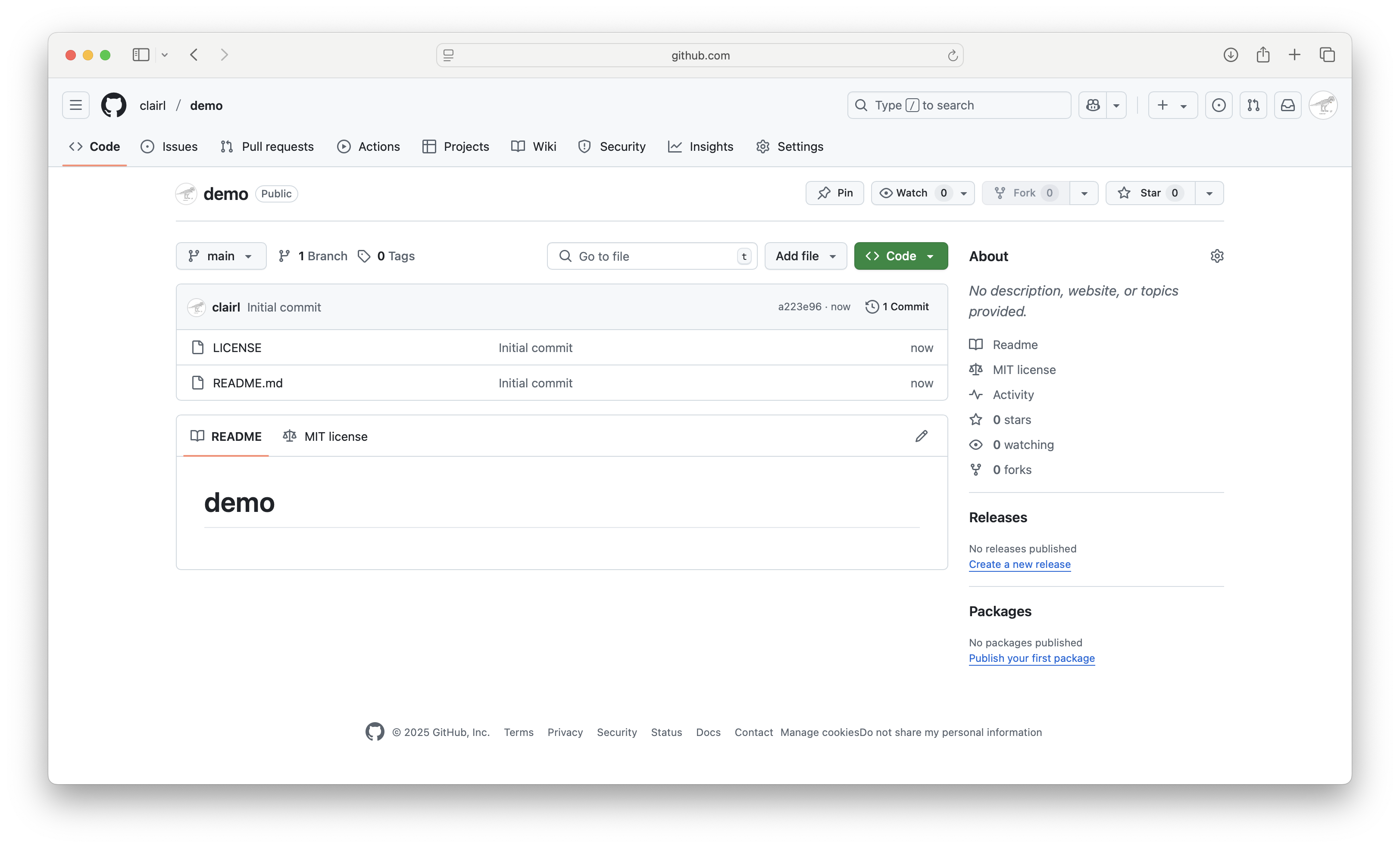
Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Git defaults to the
mainbranch

Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- The commit message and commit ID
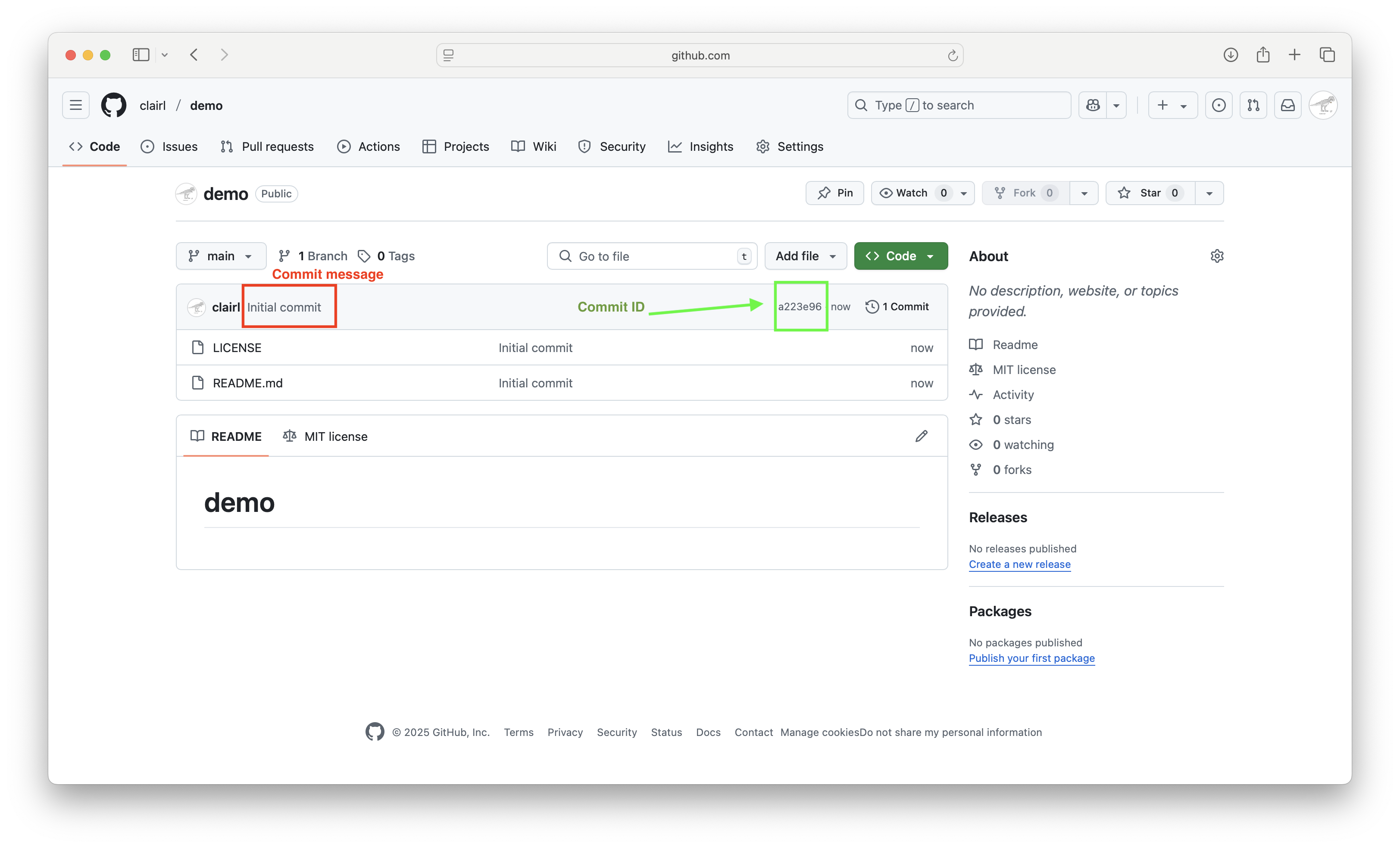
Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- Two files were created: LICENSE and README.md
- Note the files created have the same Git message

Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- LICENSE refers to the license chosen when creating the repository

Create Git Repository on GitHub (cont’d)
- README.md is the landing page for your repository
- It is where you describe your repository

Clone GitHub Repository in GitHub Desktop
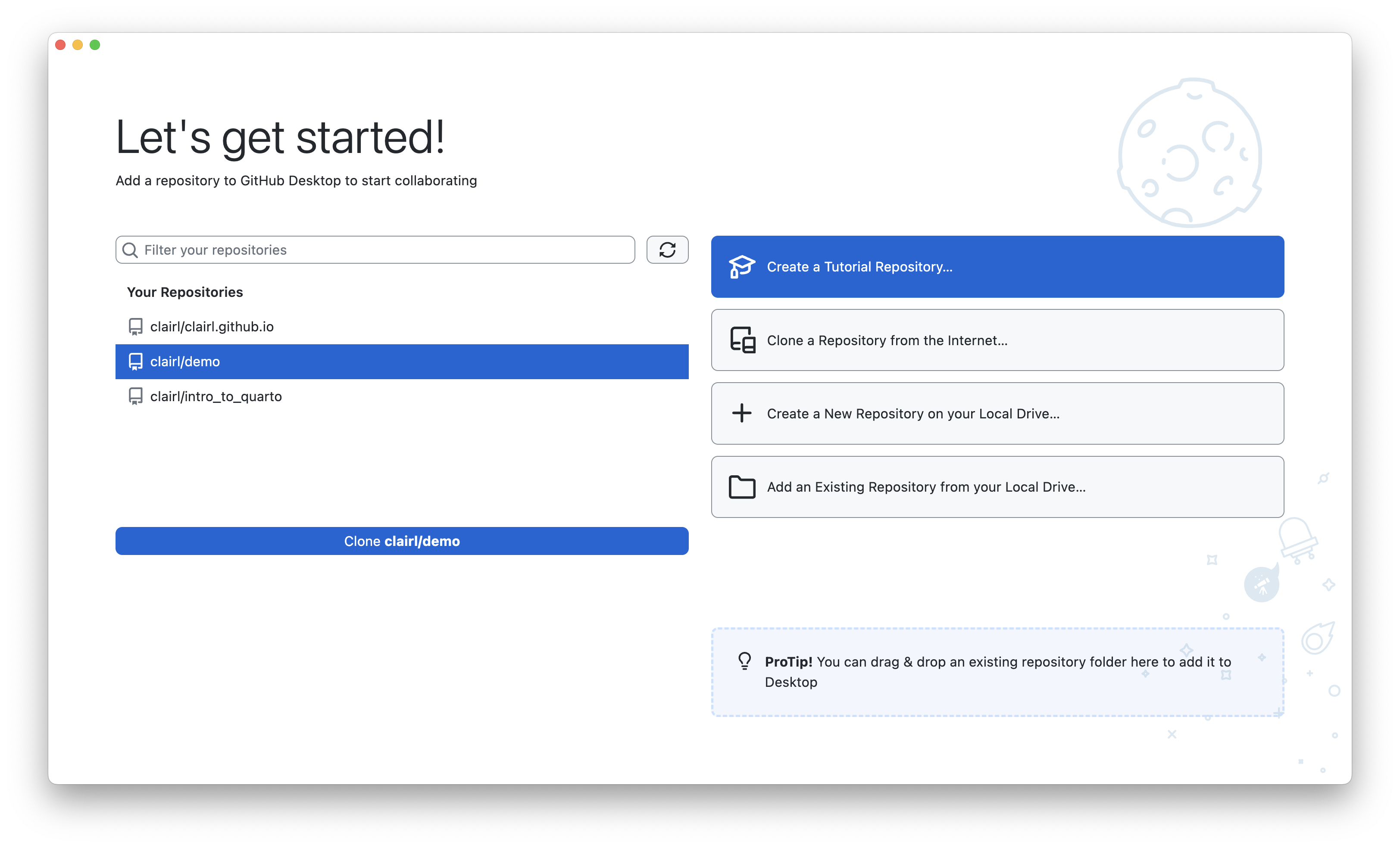
- Open GitHub Desktop and log in (if you are currently logged out)
Clone GitHub Repository in GitHub Desktop (cont’d)
- On the left-hand-side, you will notice a list of your GitHub repositories
- Choose the repository you wish to make a copy to your local computer
- Then select “Clone username/repo”, where username/repo is your GitHub username and repo is the name of the repository
- In this example it is clairl/demo
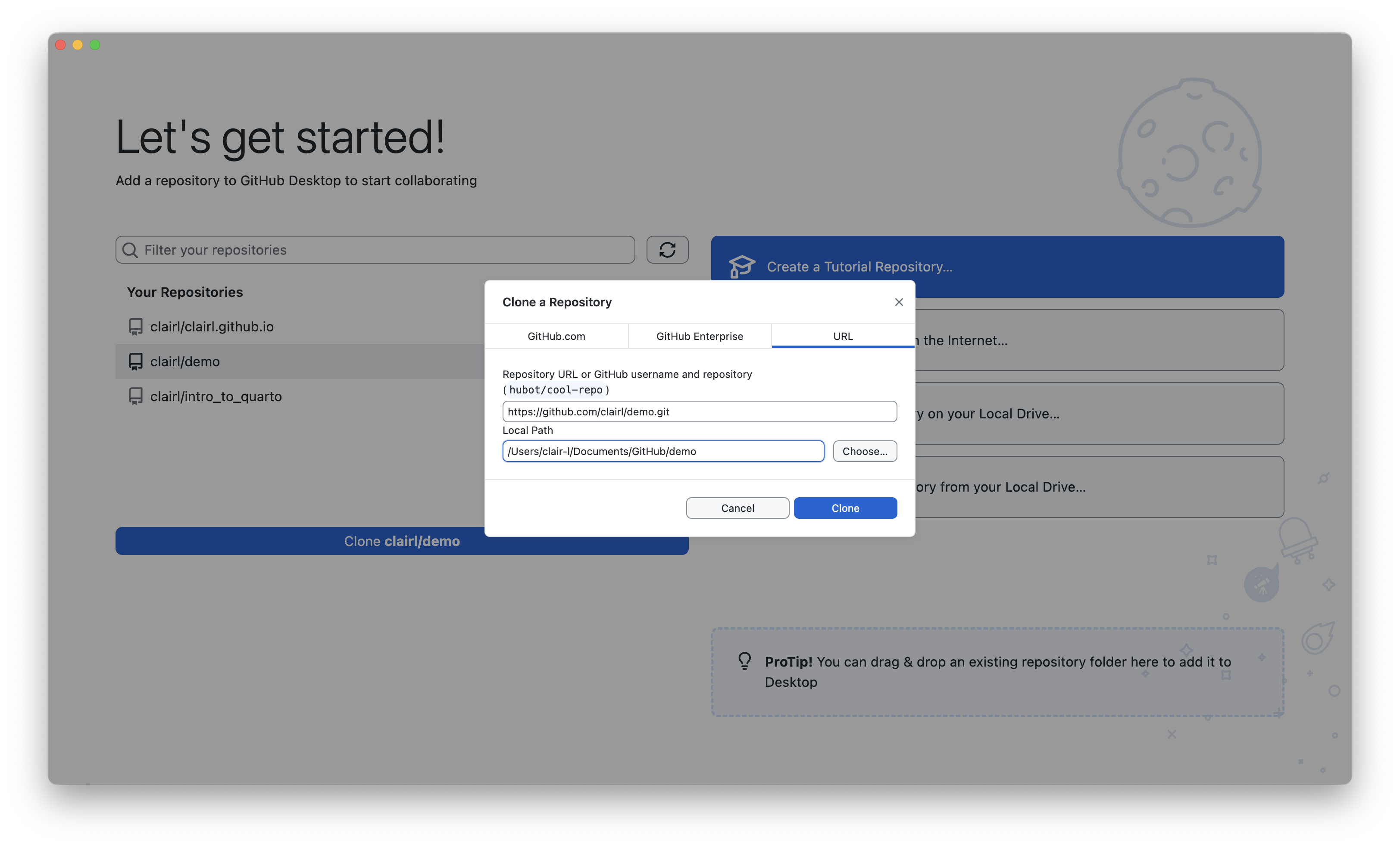
Clone GitHub Repository in GitHub Desktop (cont’d)
- Choose the location for the clone of the GitHub repo on your local computer and click Clone
Clone GitHub Repository in GitHub Desktop (cont’d)
Create a Git Repository from Existing Folder
- Say we already have a folder with files that we want to connect to GitHub?
- First, we have to enable Git
- To do this, we have to use the Terminal
Create a Git Repository from Existing Folder (cont.)
- In the terminal, navigate to the project folder
Create a Git Repository from Existing Folder (cont.)
- Use the following commands:
- The first command enables git, while the second command stages files for the next commit
- The
.means “the current directory and all its contents”
Application: Creating a Webstie Using Quarto and GitHub Pages
Workflow
- The workflow we will be using to create our website is:
- Create a new Quarto project in R Studio
- Connect our project directory to GitHub through Github Desktop
- Publish the newly created website via GitHub Pages
- Create new pages for the website
- Add a blog to the website
- Customize the website
R Projects
R Projects
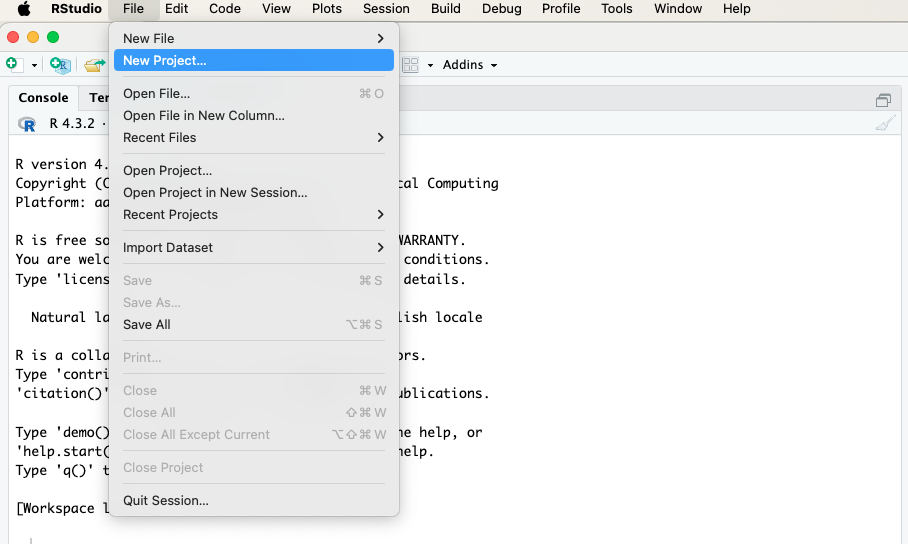
- To begin, create a new Quarto project in R Studio
- Click File->New Project…
R Projects (cont.)
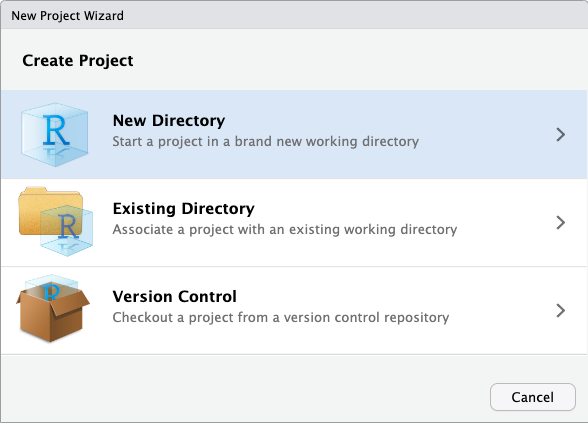
- Select New Directory
R Projects (cont.)
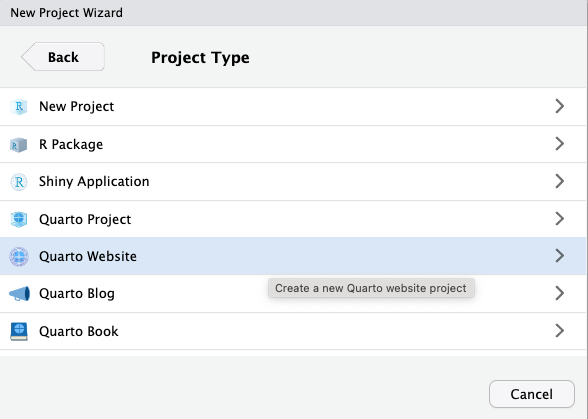
- Select Quarto Website
R Projects (cont.)
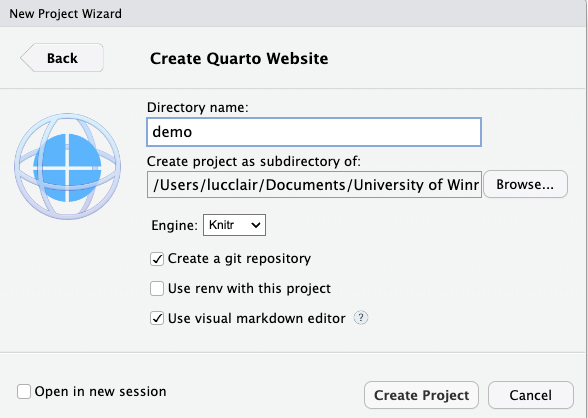
- Name the directory. I named mine demo.
- Choose a path for the new project and click Create Project
Quarto Website Files
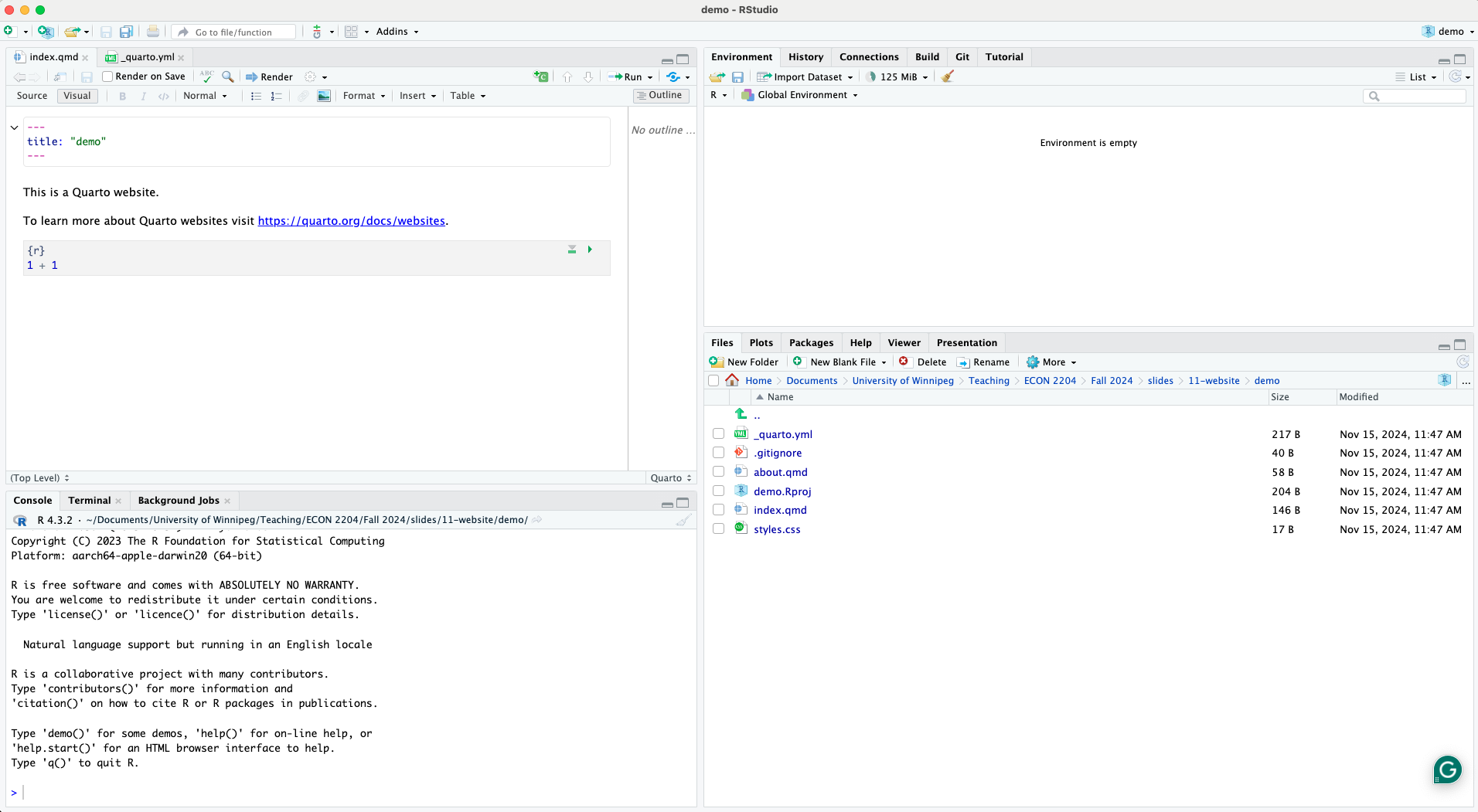
- R Studio creates a project with a number of files
Quarto Website Files (cont.)
- _quarto.yml: key configuration file for the Quarto website.
- Defines the overall structure and settings for the website project,
project: - Defines metadata for the website, e.g., title, author(s), and other descriptive info,
title:anddescription: - Controls the structure of the website,
navbar: - Specifies themes,
format:,theme:,css:
- Defines the overall structure and settings for the website project,
Quarto Website Files (cont.)
- index.qmd: home page of your Quarto website
- Defines the content and layout for the main landing page of the site
- Can add Markdown and Quarto-specific content
- Defined as Home in the _quarto.yml file
- .gitignore: configuration file used in Git repositories to specify intentionally untracked files or directories that Git should ignore.
Quarto Website Files (cont.)
- about.qmd: Quarto Markdown file that is typically used to create an About page for a Quarto website.
- This page provides information about the website’s purpose, the author(s), or the organization behind it.
- Not mandatory
- Appears as another page on the navigation bar
- style.css: Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) file used to define and customize the visual appearance of a Quarto website or document.
- allows you to override or extend the default styles provided by Quarto’s themes
Building the Website
To build the website, click the Render button at the top of the index.qmd file.
Alternatively, you can also click Build, then Render Website in the top right pane.
Building the Website (cont.)
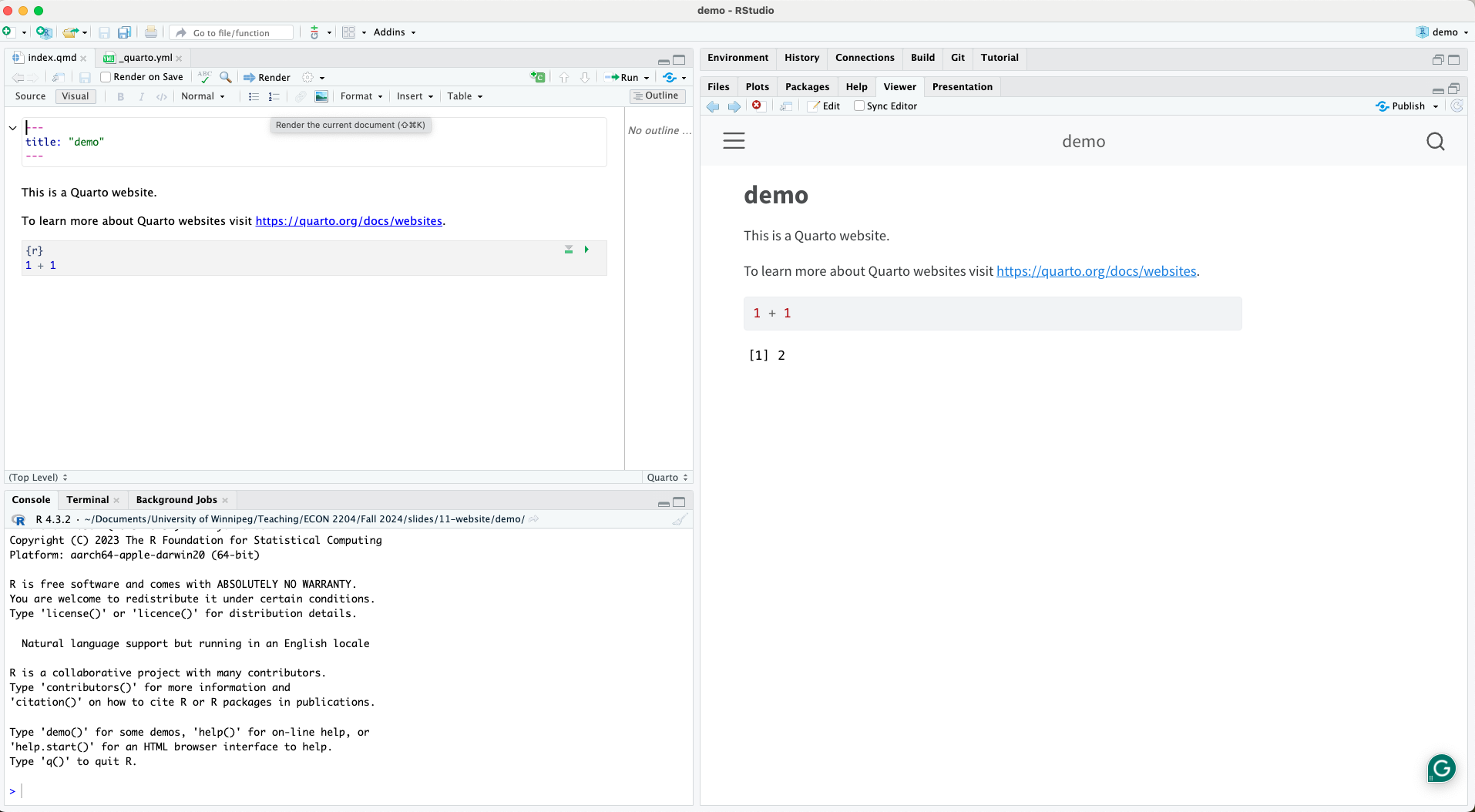
Connecting R Project to GitHub
Connecting R Project to GitHub
Before we can publish our website, we need to connect our R project to a GitHub repository
Be sure that you are signed into your GitHub account in GitHub Desktop.
Open GitHub Desktop and add the R project Directory
- Select Add Existing Repository
- Choose the R project directory
Connecting R Project to GitHub (cont.)
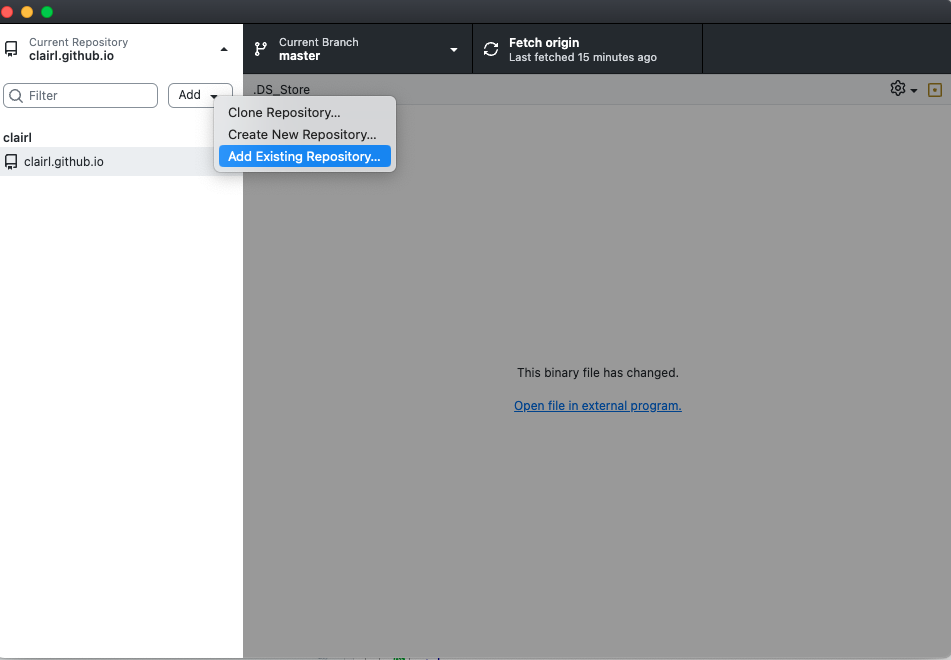
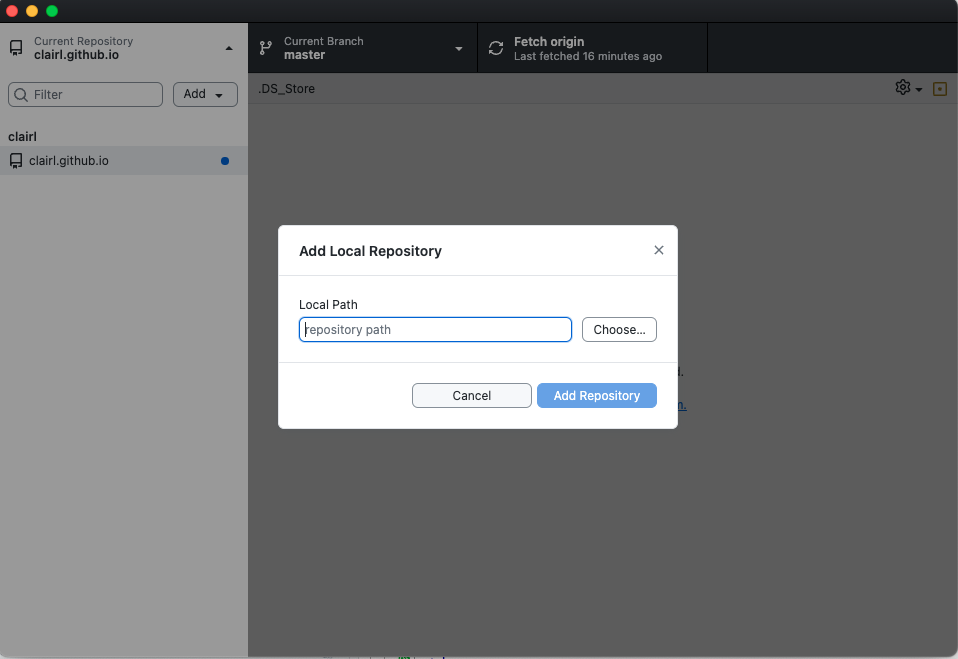
Connecting R Project to GitHub (cont.)
- Commit changes
- Write a summary (E.g., “Created Quarto website”)
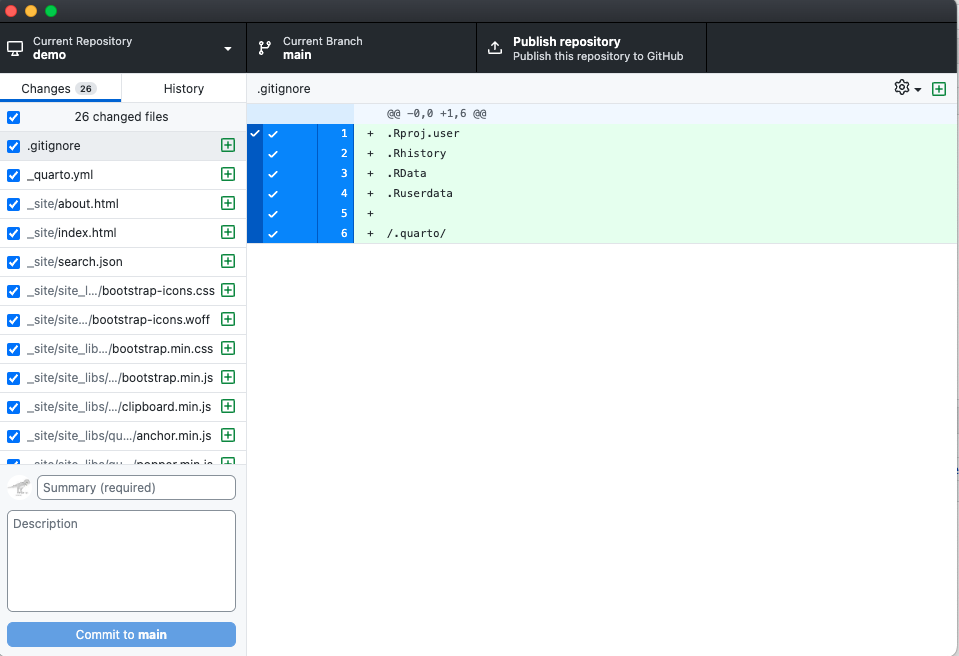
Connecting R Project to GitHub (cont.)
- Publish repository to GitHub.com
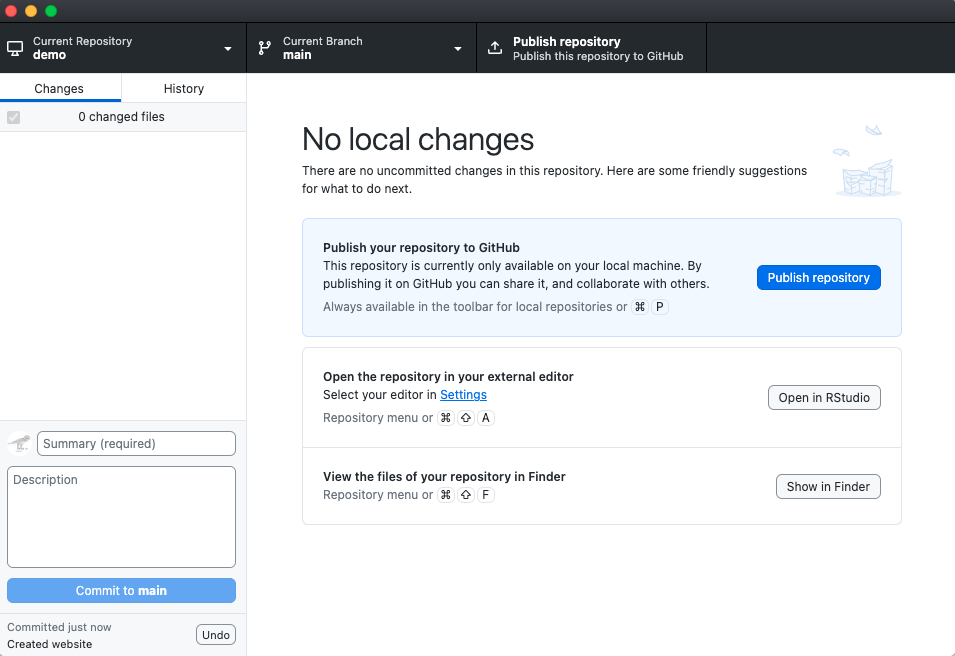
Connecting R Project to GitHub (cont.)
- Go to GitHub.com to confirm that the repository has been published.
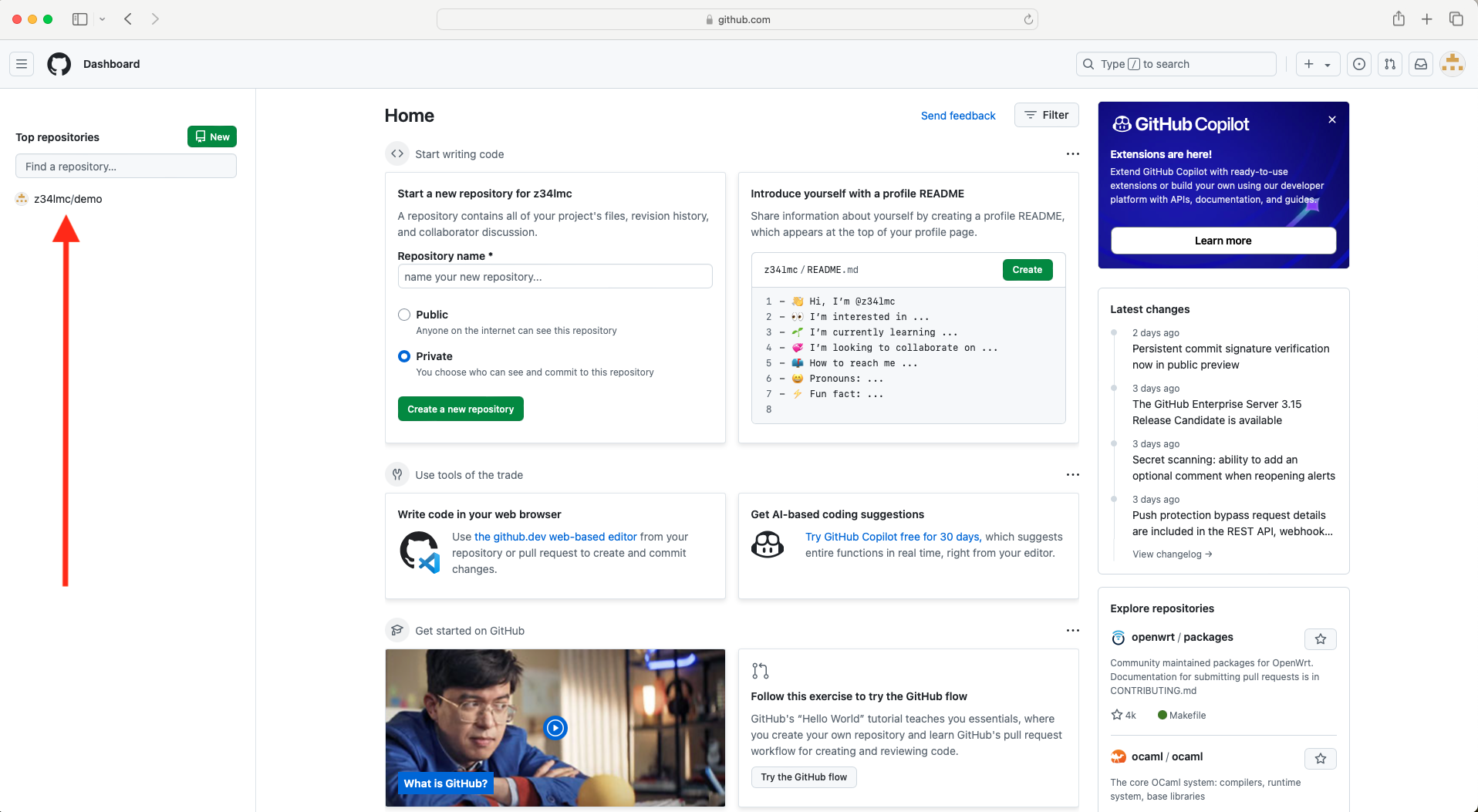
Connecting R Project to GitHub (cont.)
- Check to see that the project files are now available in your repository
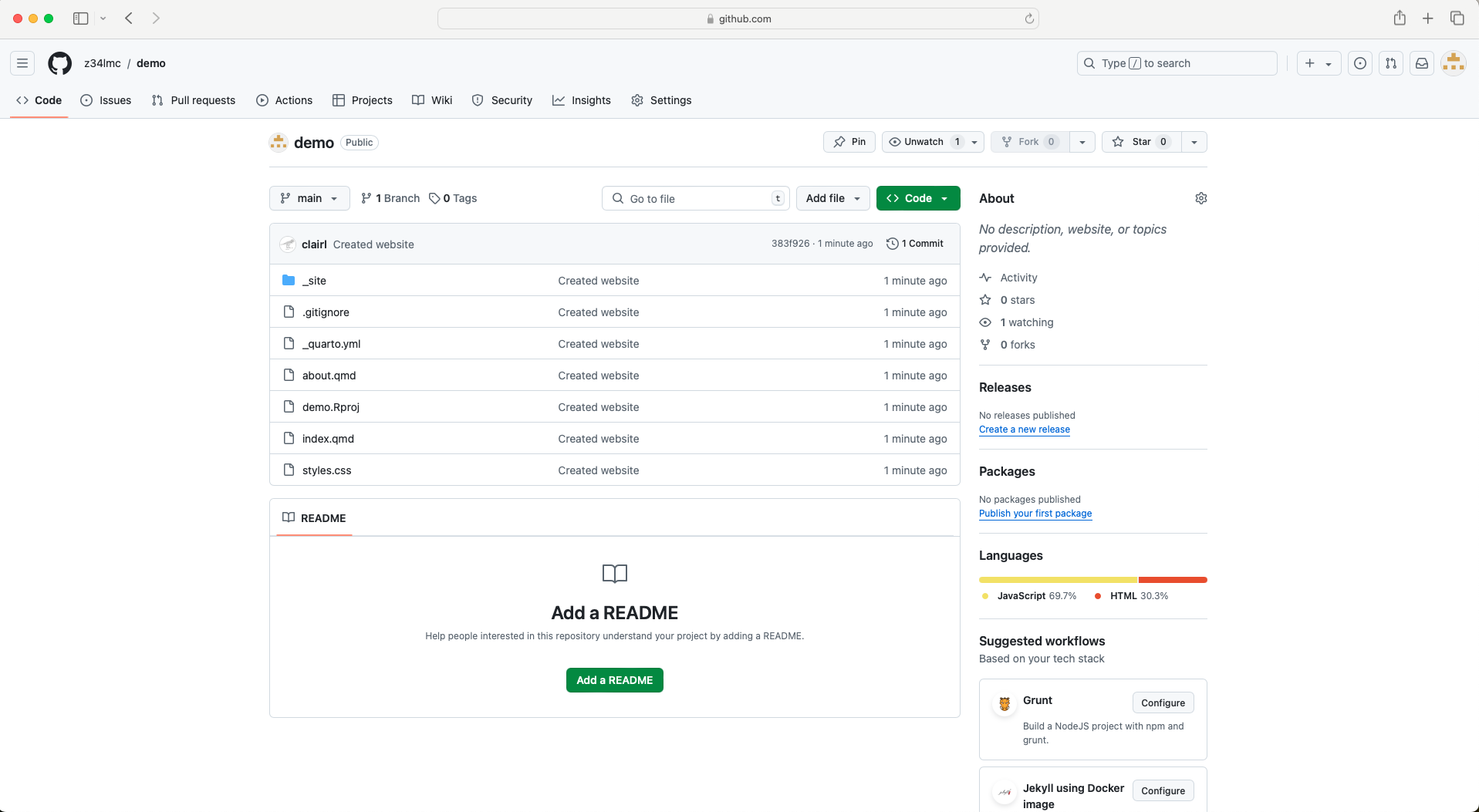
Publishing Your Website
Publishing Your Website
- Return to R Studio and open the _quarto.yml file.
- Under
project:include the codeoutput-dir: docsand render the website. This will save the website files in a newly created docs folder.
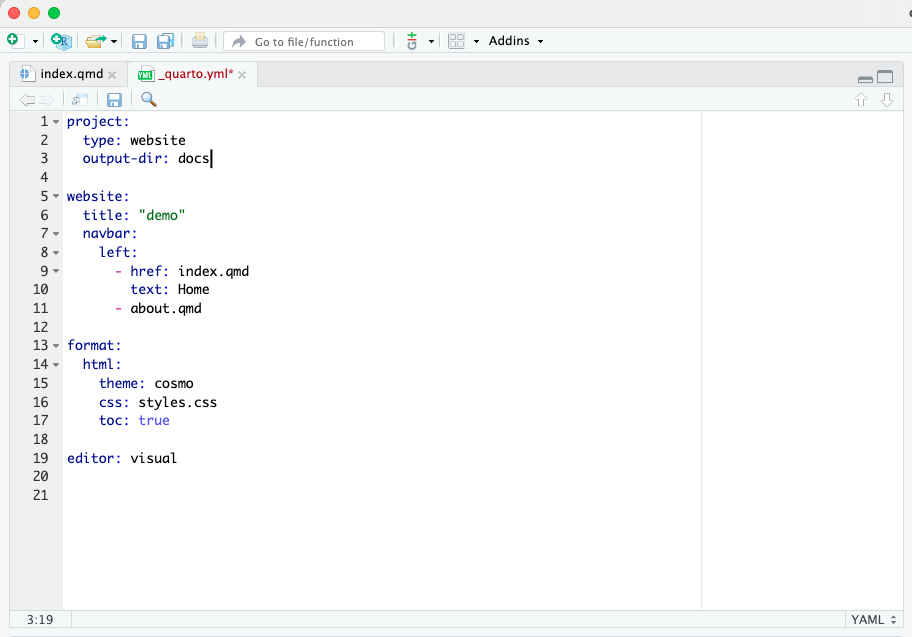
Publishing Your Website (cont.)
- We no longer need the _site folder, so we can delete it.
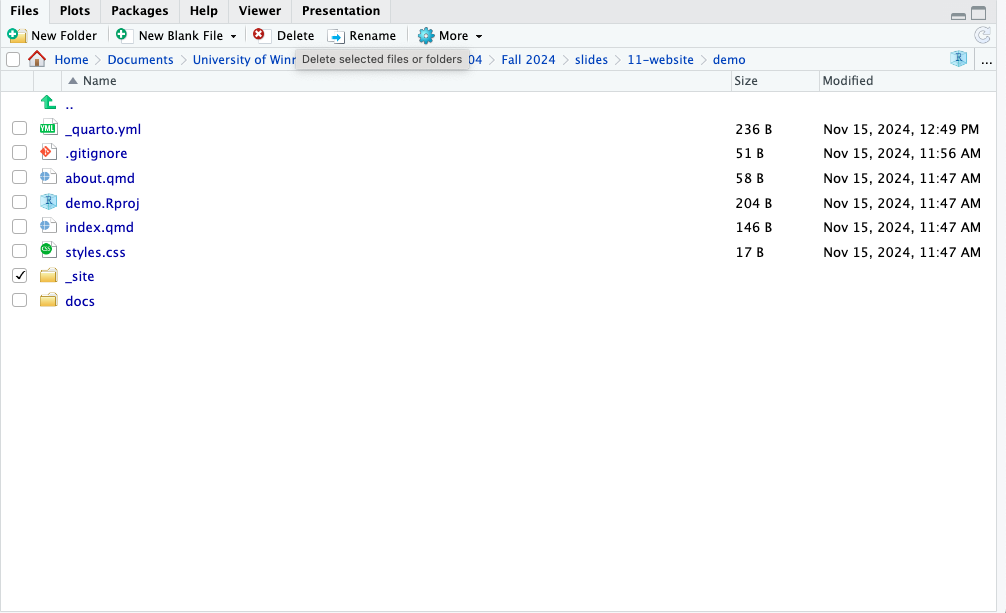
Publishing Your Website (cont.)
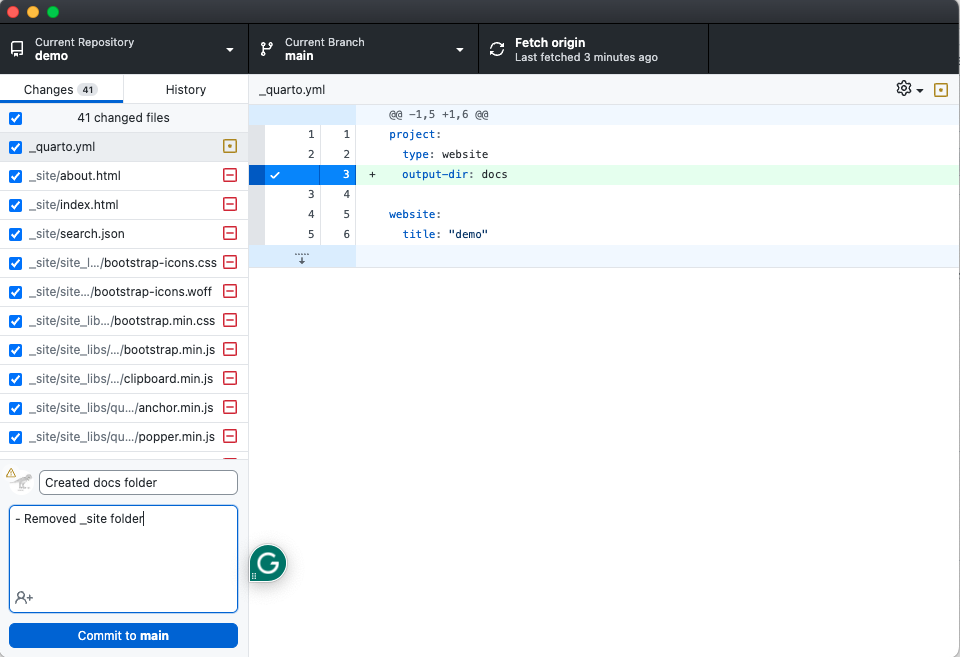
- Return to GitHub Desktop, commit the changes, and push them to GitHub.com.
- Remember to leave a summary
Publishing Your Website (cont.)
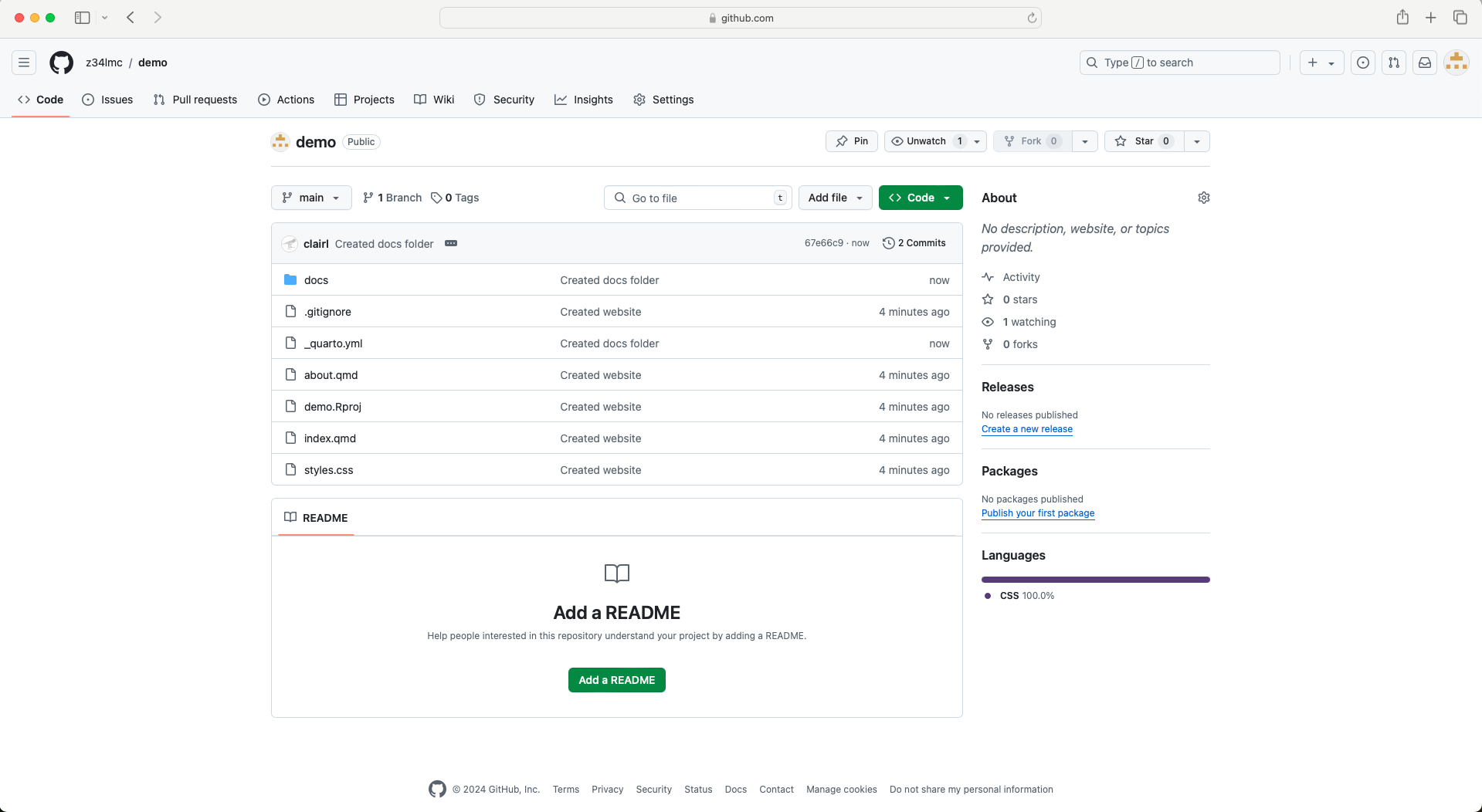
- Return to GitHub.com.
- Note that the docs folder has replaced the _site folder.
GitHub Pages
- Click Settings from the top menu.
GitHub Pages (cont.)
- Choose Pages from the menu on the left-hand-side
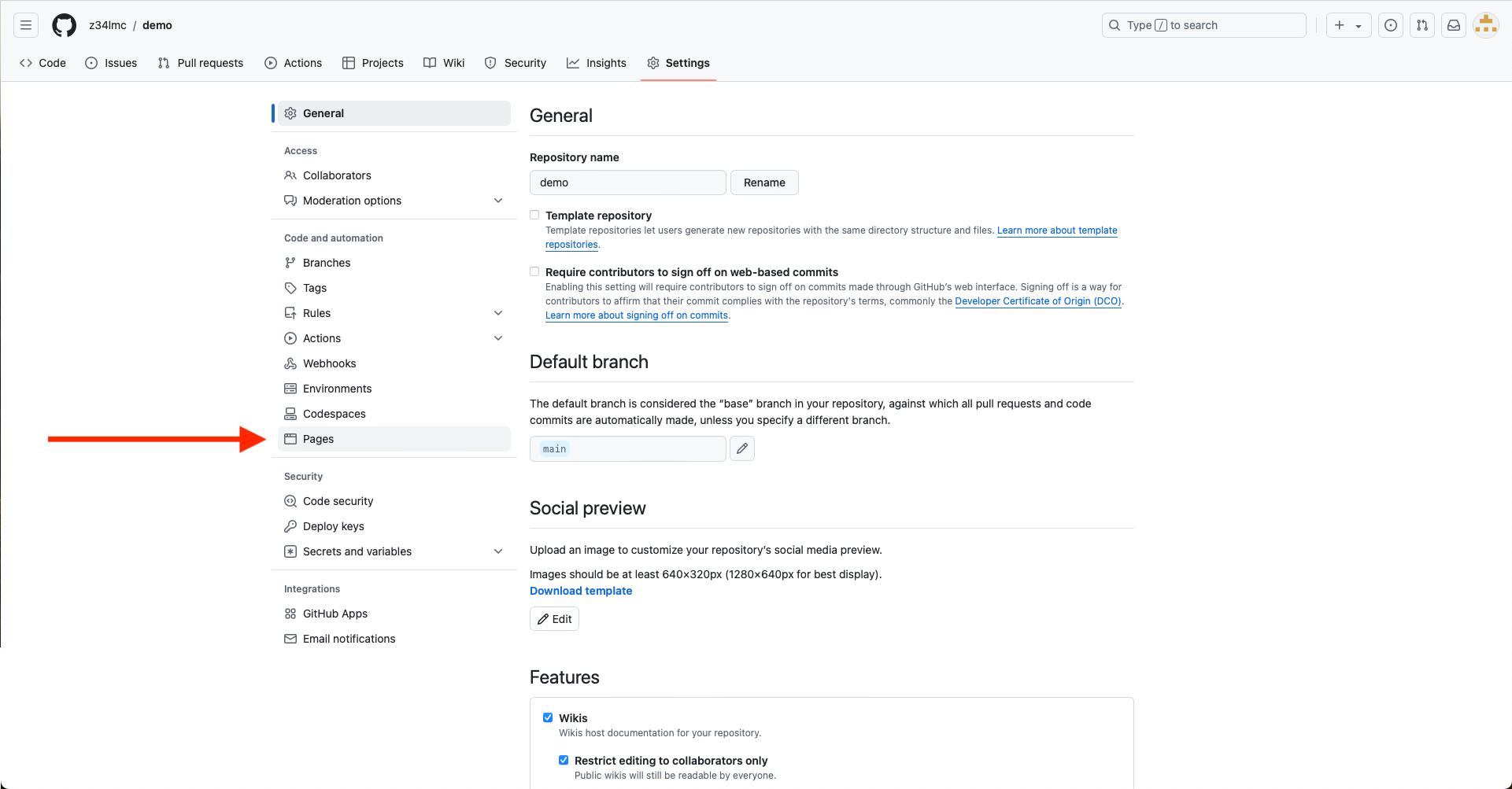
GitHub Pages (cont.)
- Set the branch to main
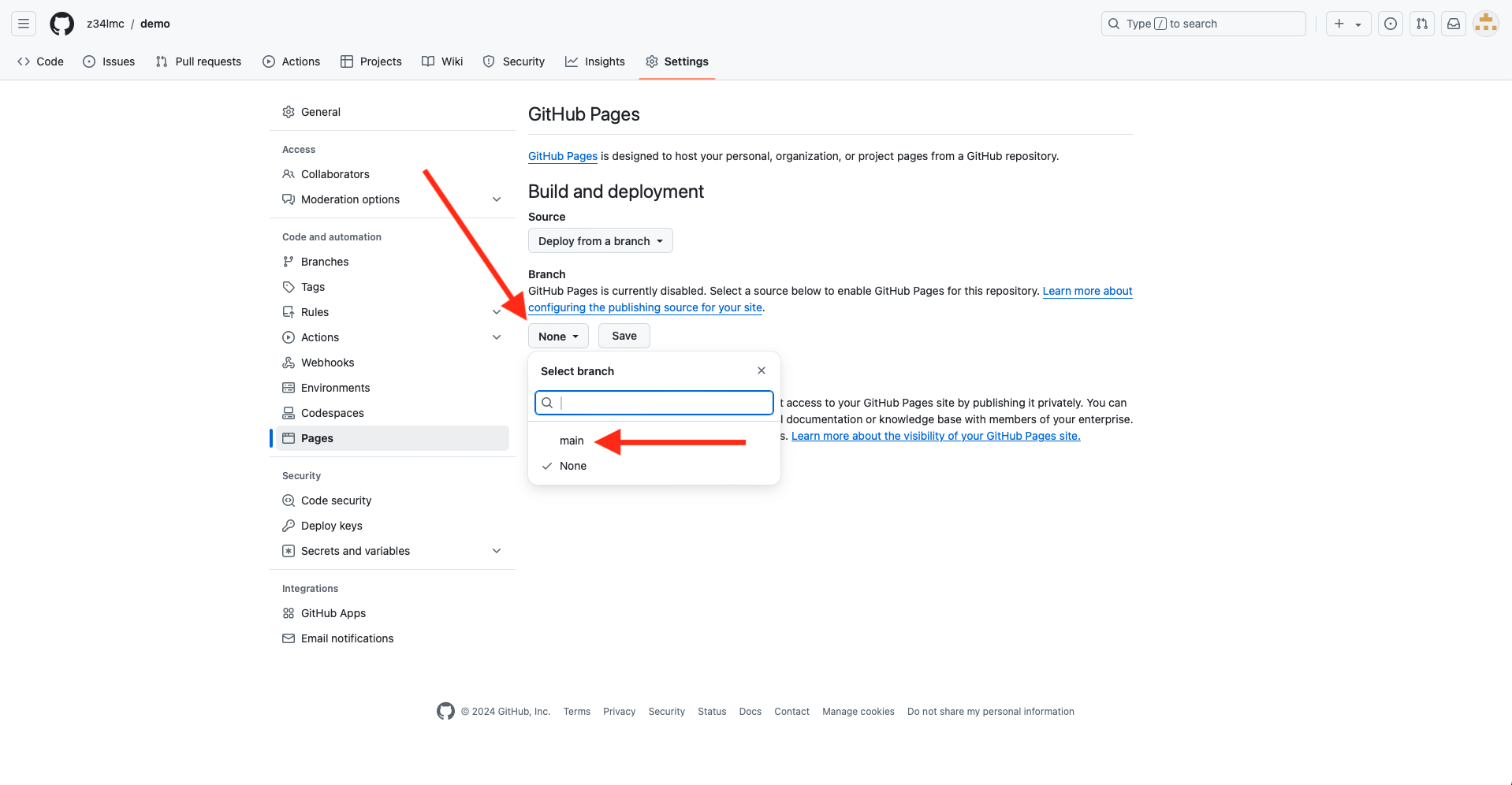
GitHub Pages (cont.)
- Set the folder to docs
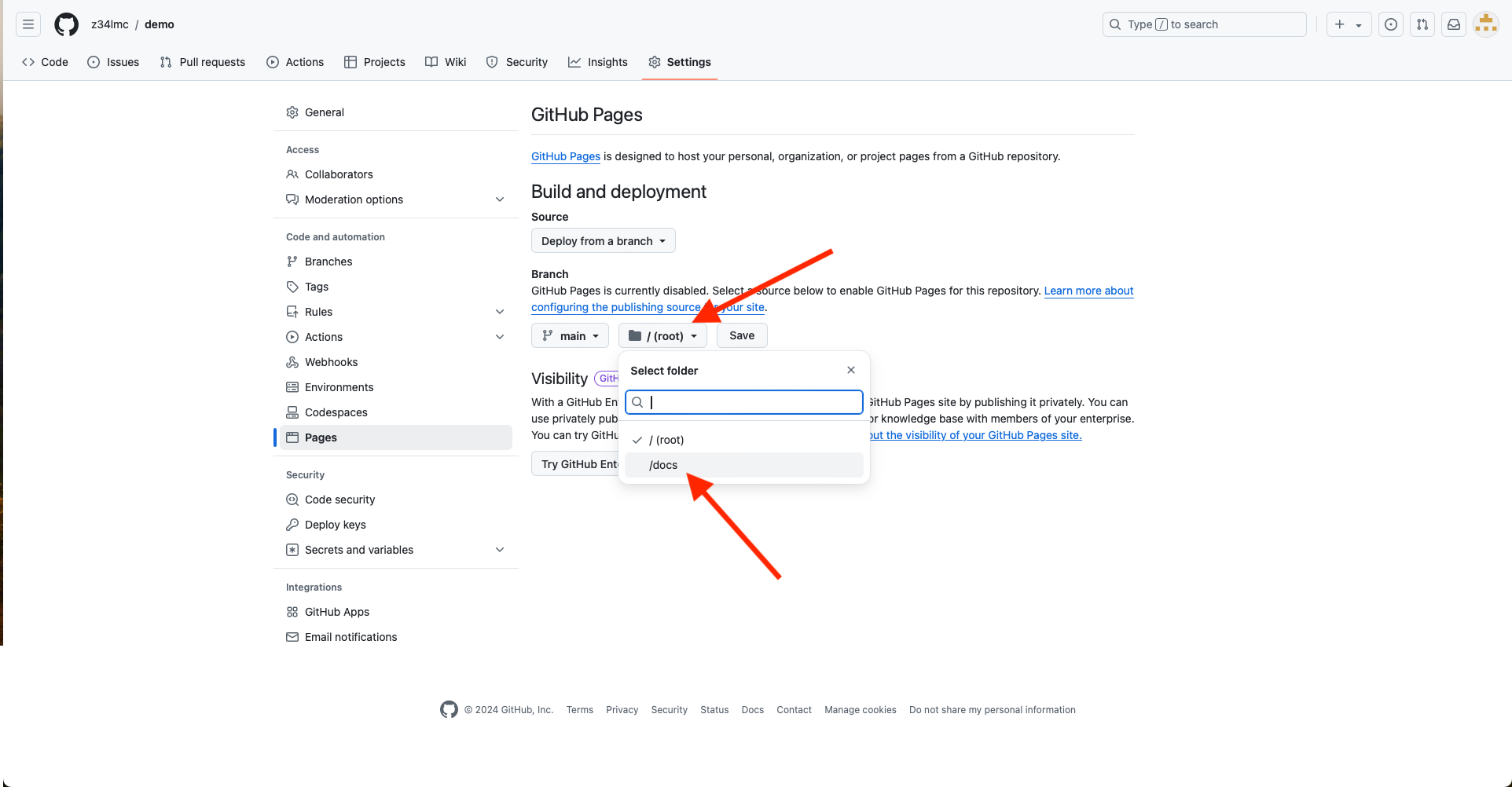
GitHub Pages (cont.)
- Note the message saying that the website is being built
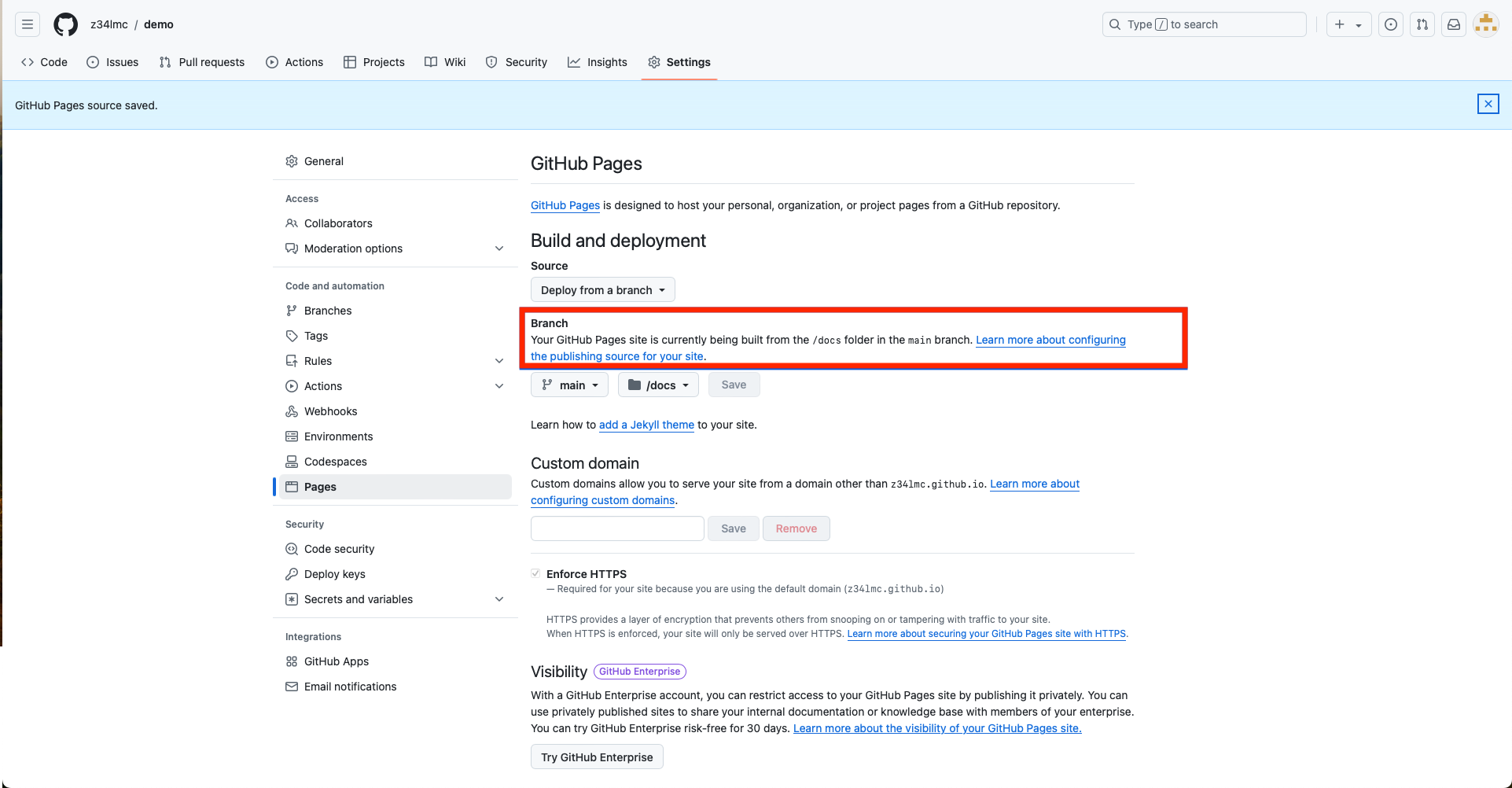
GitHub Pages (cont.)
- Wait a about a minute, then refresh the page. You should see a message that the site is live at a given URL.
- The URL is typically https://username.github.io/repository_name
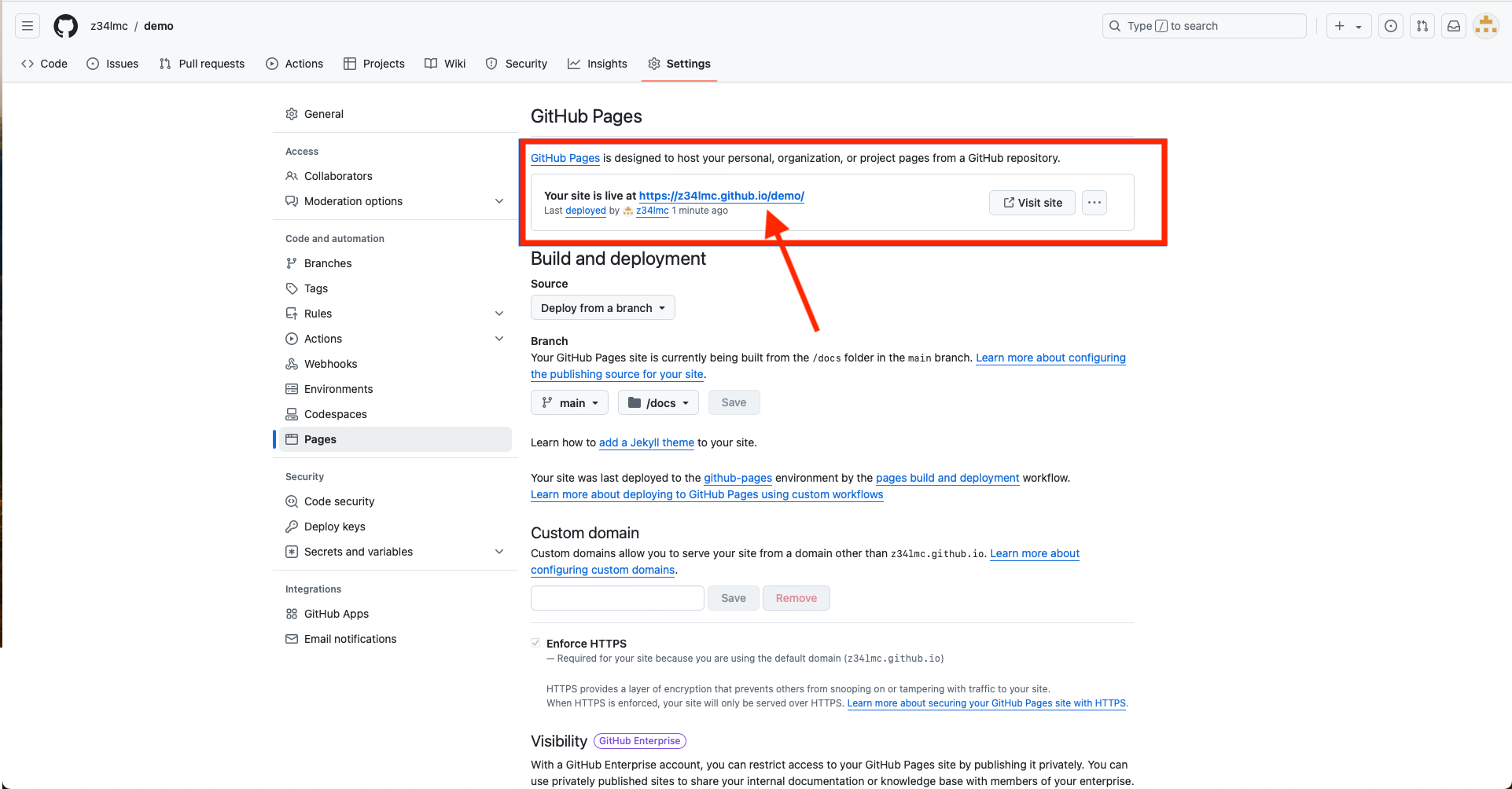
Publishing Your Website (cont.)
- Follow the link to view your website
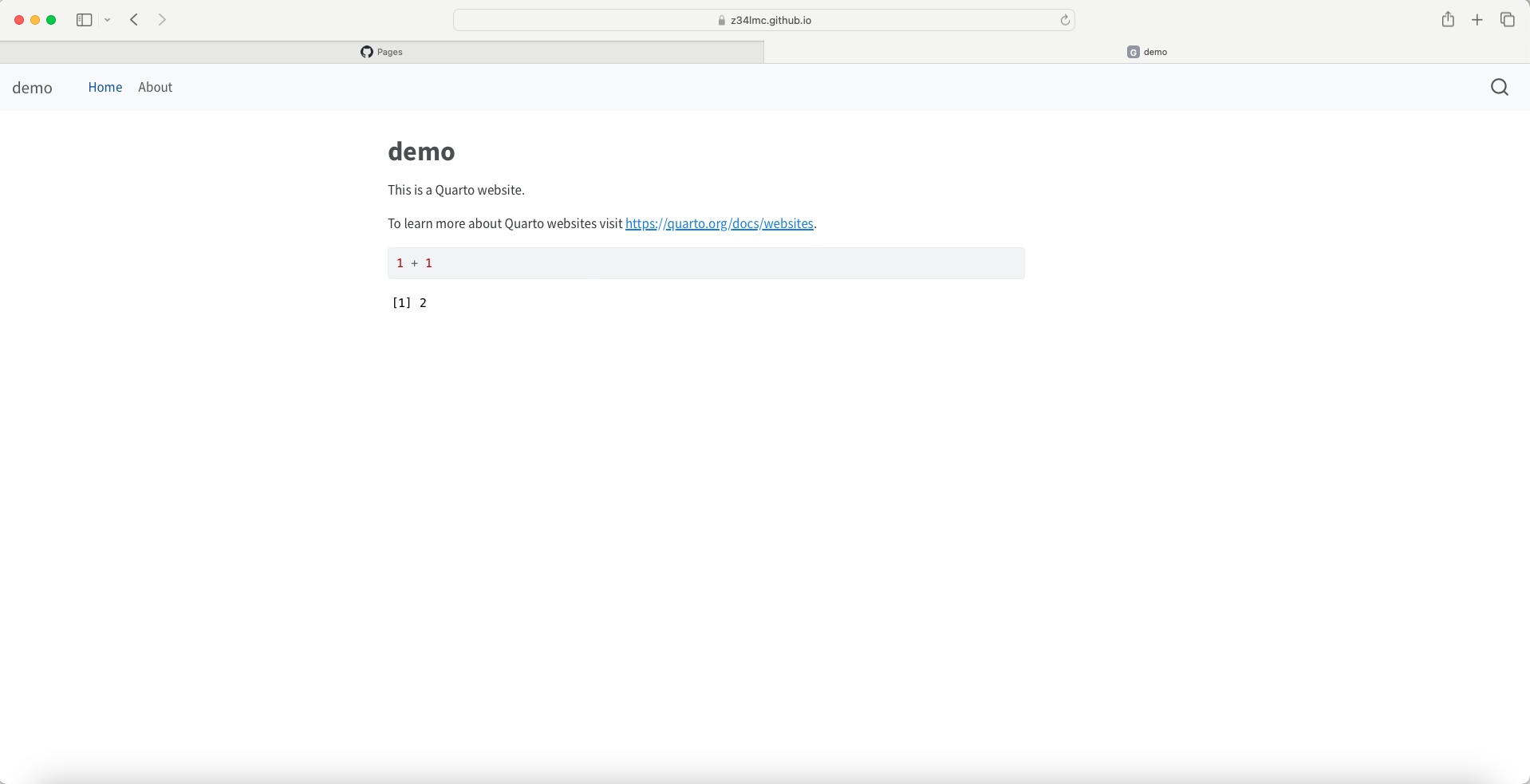
Adding Pages to Your Website
Adding Pages to Your Website
- To add a webpage, create a new .qmd file and save it in your project directory.
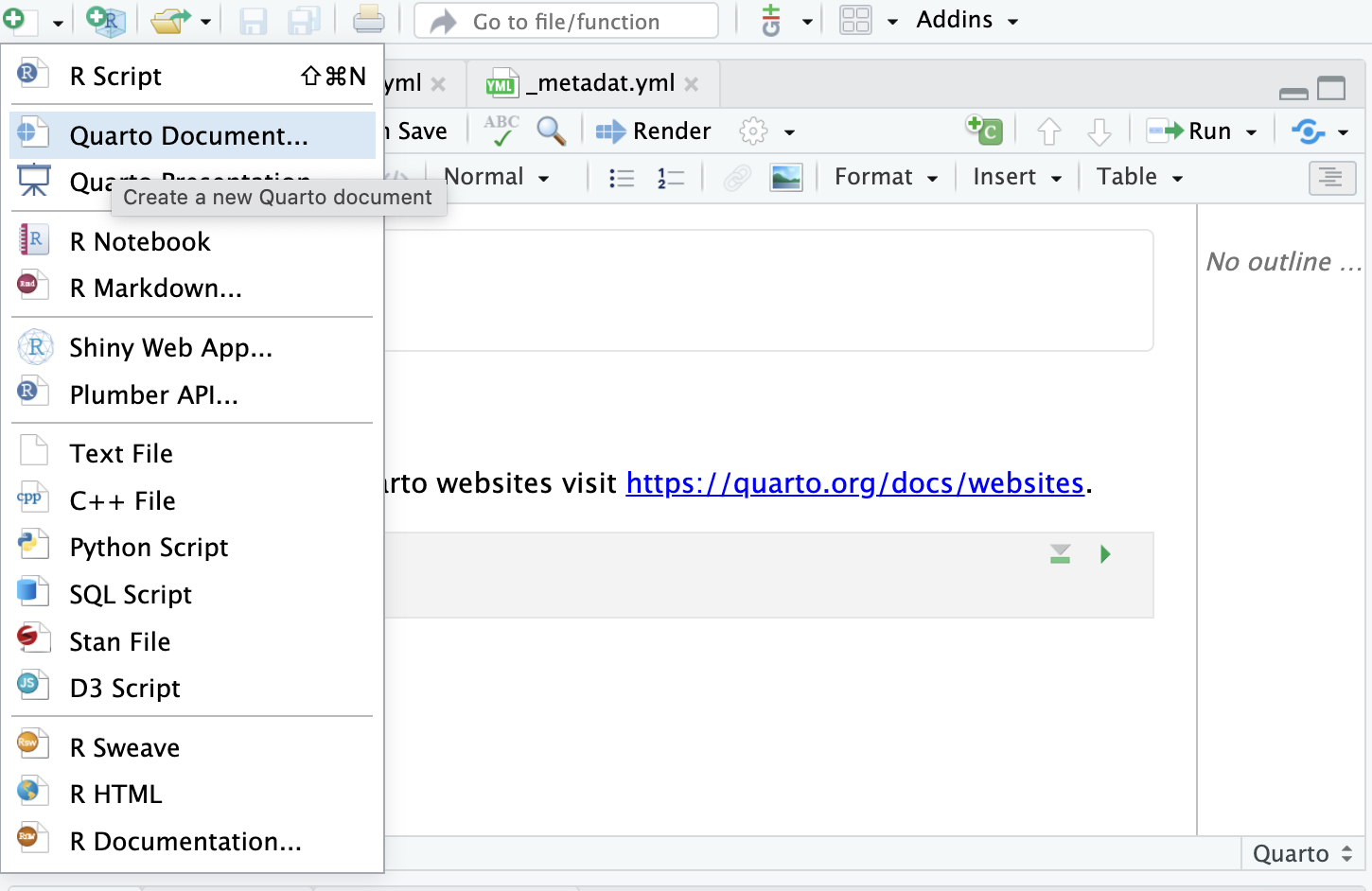
Adding Pages to Your Website (cont.)

Adding Pages to Your Website (cont.)
- Add the new Quarto file to the navigation bar in the _quarto.yml file
href:adds the listing page file to the navigation bartext:is the text that will display on the navigation bar.
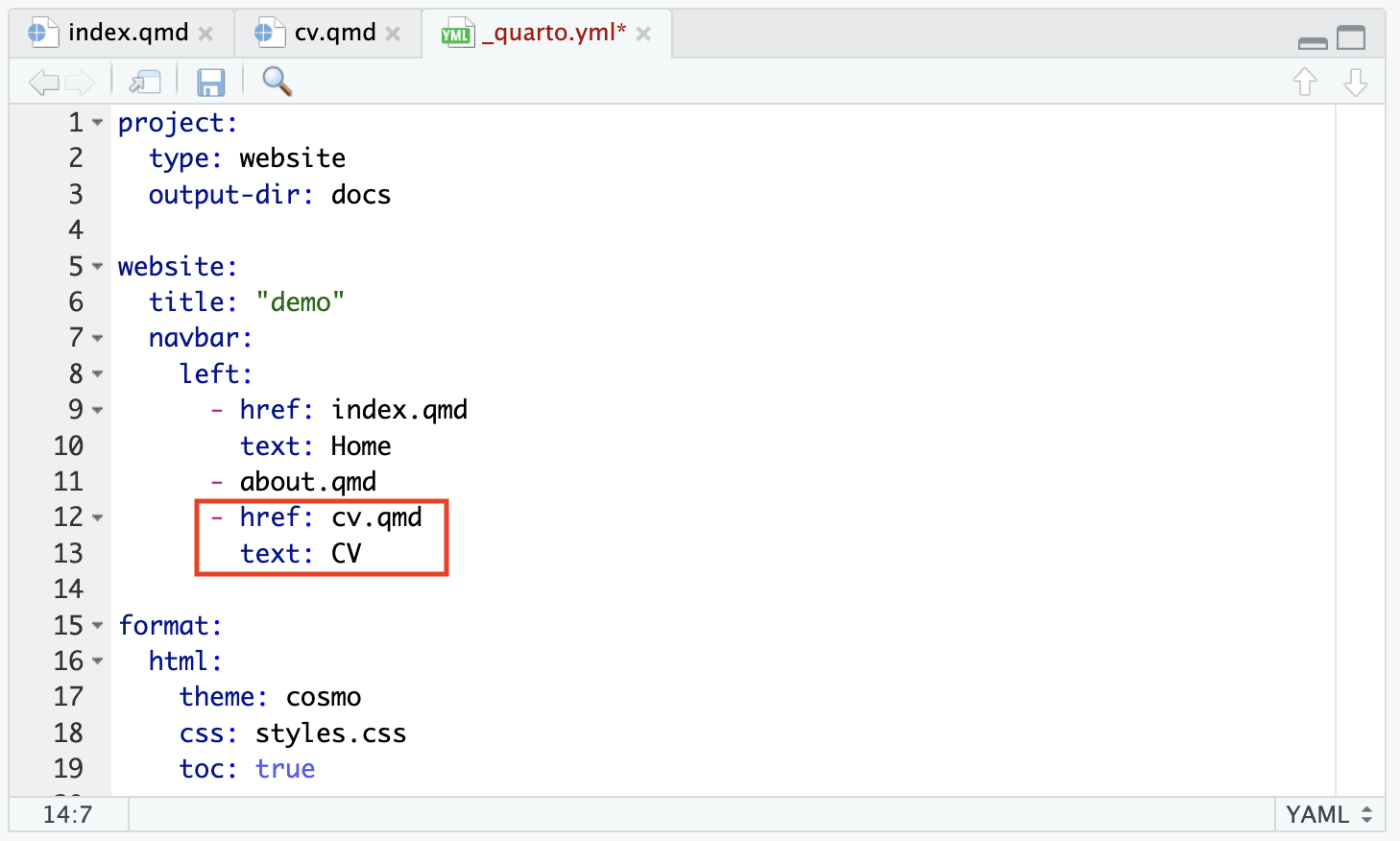
Adding Pages to Your Website (cont.)

Add File to a Webpage
Add File to a Webpage
- You may want to include downloadable file formats on your website
- Add the file to your project directory and reference it within your Quarto document.
- It is helpful to create sub directories to store your files,e.g.,
- Figures: store figures
- Data: datasets
- Files: pdf documents
Add File to a Webpage (cont.)
- Reference the file using the syntax
 - E.g.,

Add File to a Webpage (cont.)

 button
button